Many people suffer from seizures for a variety of reasons. Whether it’s due to genetics or a health condition developed later on in life, seizures can be an extremely troubling and exhaustive experience.
Some people know what triggers their seizures, while others occur at random, unprovoked periods. Regardless of how often they occur, many people rely on medication to help keep their seizures at bay.
There are numerous anticonvulsant medications available to help treat seizures, which also have a direct correlation to nerve pain.
Nerve pain can range from mild to more severe, and for extended periods of time, it can severely affect a person’s quality of life.
This article will examine the benefits of anticonvulsant medication and how it can help those suffering from nerve pain and seizures.
Seizures and Nerve Pain
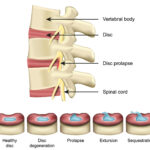
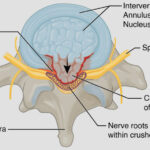
Nerves can easily become damaged, but the healing process can be drawn out and relatively difficult. Damage in nerves can occur from injury, disease, toxins, and surgery.
There are also quite a few health problems that can lead to nerve damage.
Some of these health conditions include:
- Shingles
- Diabetes
- Herniated disks
It’s also known that anticonvulsants can help with issues like chronic pain and fibromyalgia. The way these medications work is by interfering with overactive pain signals from sensitized or damaged nerves. With different types of anticonvulsant medication come various use cases.
There isn’t a universal application for such medications, and many of them are only prescribed to those with specific health concerns.
Nevertheless, no one should have to suffer from nerve damage caused by seizures or other health complications like those mentioned above.
From children to adults, nerve damage is something that can happen at any stage during your life.
Whether it’s from a traumatic injury, illness, or genetic condition, managing issues with nerve damage can be painful and tiresome.
Utilizing the benefits of anticonvulsants can help ward off the effects of nerve damage, manage seizures, and benefit the quality of life for each individual.
What are the Different Types of Anticonvulsants?
The treatment of seizures and nerve pain isn’t a new concept and has been studied for years. Due to this, many anticonvulsant medications are known to be relatively safe for a wide variety of different conditions and patients.
Depending on the type of nerve pain you’re experiencing, a doctor may prescribe one of the following anticonvulsant medications.
- Lamotrigine (Lamictal)
- Valproic acid (Valproic)
- Carbamazepine (Tegretol)
- Phenytoin (Phenytek, Dilantin)
- Oxcarbazepine (Trileptal)
- Pregabalin (Lyrica)
- Topiramate (Topamax)
- Gabapentin (Neurontin)
- Ethosuximide (Zarontin)
It’s common for follow-up visits to be needed after taking such medication.
Regardless if taken in the short or long term, it’s important to pay attention to changes in seizures or nerve damage over time. Many of these medications only offer benefits when used for extended periods of time.
In the same vein, potential health risks and complications should be considered before taking any of these medications.
Possible health risks associated with such medications include:
- Vomiting
- Double vision
- Liver damage
- Headaches
- Loss of coordination
- Nausea
- Drowsiness
If left unchecked, many of these side effects could worsen over time. When taking anticonvulsant medication for the first time, discovering what works best for each person may require trial and error.
It’s also vital to note that you shouldn’t blend these medications to avoid any adverse effects on your health.
Dealing with nerve damage and seizures can be a debilitating process that’s hard to manage, and some of these medications may not be right for the patient.
Nevertheless, the potential risks and side effects are pretty minimal, and the medications listed above are known to be quite helpful.
A Deep Dive on Adverse Effects
There’s plenty of data that highlights the potential adverse effects of taking anticonvulsants. The possibility of experiencing such events ranges from 7% to 31% and is generally mild for the most part.
You should also consider that allergic reactions are a possibility with any medication, even if these chances are slim with anticonvulsants.
However, those who partake in chronic use of such medications can end up developing osteoporosis.
To help avoid such issues, it’s suggested to utilize calcium and vitamin D supplements in addition to regular exercise.
Working against the effects of nerve damage comes with a long road, but it’s entirely possible to manage.
It’s also crucial to note that many anticonvulsant medications are known to potentially cause suicidal thoughts in patients. This comes with a low risk, but it shouldn’t be disregarded by any means.
More serious side effects known to be correlated to anticonvulsants include:
- Psychosis
- Lupus syndrome
- Hepatic failure
- Aplastic anemia
- And a few others
There may be many nuances related to taking anticonvulsant medications, but seeking help from a medical professional is the best course of action.
They’ll be able to administer the right drug for the patient’s needs while educating you on necessary precautions to consider beforehand.
The Bottom Line
With the extensive amount of research available for anticonvulsants, they can be seen as a generally safe option to fight against the effects of nerve damage.
Any medication should be taken with caution, but anticonvulsants have improved the lives of many on a global scale, regardless of health conditions, age, or genetics.