This may not be a widely known disease among the general public, but it’s extremely common in regard to chronic rheumatic diseases.
It’s specifically found in children, and it’s characterized by peripheral arthritis.
There are a few subgroups that juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) is divided into.
Demographic characteristics, treatment approaches, disease prognosis, and clinical features are all a part of this.
Some common recurrences with this disease are fevers and rashes. Considering the sensitivity of many children, JIA can feel like an extremely troublesome disease.
Continue reading through this article to learn important facts about JIA, the groups it affects, and how it affects the health of children.
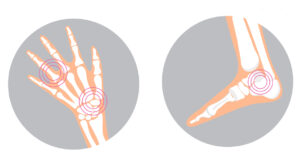

Understanding the Basics
JIA shows itself in many different ways with a variety of symptoms. In young females, oligoarticular JIA is commonly found and usually comes with positive anti-nuclear antibodies. It also comes with anterior uveitis.
With seropositive polyarticular JIA, you’ll find similarities with adult rheumatoid arthritis, but it only affects roughly 10% of young patients.
Various symptoms of arthritis can be found with the disease, and they can affect children in a variety of ways. Some associated symptoms include the following:
- Arthritis
- Nail pitting
- Psoriatic rash
- Dactylitis
The effects of JIA can change over time as well. Certain health complications related to JIA pertain to osteoporosis, growth retardation, and macrophage activation syndrome, which can be life-threatening.
Treatment of this disease is quite complex and requires long-term effort from all parties involved. It usually consists of substantial help from numerous medical professionals, with the patient and the family playing their part.
Without the right amount of medical attention, JIA can be properly managed. However, if it’s left untreated, it can lead to debilitating health concerns that could significantly affect the quality of life for the patient.
With the different types of JIA, this may require specific treatment plans depending on the symptoms at hand. Each type of JIA are as follows:
- Systemic
- Polyarticular
- Oligoarticular
- Enthesitis-related
- Psoriatic
- Undifferentiated
Before diving into treatment solutions, it’s essential to take a look at the underlying influences of such a disease. These can vary greatly, just like the disease subtypes, but there’s enough research to support where JIA comes from.
Causes and Diagnosis of JIA
For starters, JIA is an autoimmune disease. Those suffering from JIA tend to deal with inflammation, such as irritation and swelling in the body, which occurs primarily in the joints.
Of course, there are many other health concerns related to JIA, but the cause is pretty straightforward.
Medical experts feel the disease comes from a combination of the following issues:
- An infection
- Genetics
- How the immune system responds to infection
Although there’s a lot of research on the disease, many doctors and medical experts agree more research is needed to fully understand JIA. The diagnosis of JIA comes with many unique nuances of its own.
Doctors can diagnose JIA through examination, looking at family medical history, or ordering a variety of blood tests.
These blood tests may include checking for inflammation, anemia, and markers for autoimmune illnesses.
There’s always the potential for the diagnosis of JIA to be a drawn-out process. Parents should understand there’s no quick fix for such a disease, and some complications may be lifelong.
Nevertheless, management of the disease is possible, but it starts with understanding the subtype and symptoms associated with it.
When looking into treatment for JIA, this generally includes the help of a few specialists.
Children dealing with JIA need the help of a care team that’s able to help with a few primary focal points. You can rest assured that those involved are well-versed in dealing with JIA.
There are a few go-to’s related to treating the disease, but it’s important that the child gets customized care for their specific subtype and associated symptoms.
Treatment Options for JIA
Regardless of the JIA subtype, treatment usually requires the help of a multidisciplinary team. Medical experts like a rheumatologist, physical therapists, primary care physicians, and ophthalmologists may be needed.
Numerous symptoms are associated with different types of JIA, but the medical team’s goal is pretty straightforward.
Medical experts will want to focus on reducing inflammation and pain and improving flexibility and strength while preventing joint damage.
In extreme circumstances, there’s a possibility for surgical invention to take place. This is particularly necessary to work on damage to the joints.
Overall, the main focus of this care team is to work on managing symptoms, preserving joint health, and improving general functionality.
Final Notes
JIA and its subtypes can be rather debilitating for young children, and it’s imperative that parents take the initiative to get the treatment they need.
Even if certain aspects of the disease’s symptoms can’t be eliminated, managing it is essential for the long-term outlook on their health.
It can include a stressful and somewhat daunting journey, but there’s more than enough help available to improve the lives of the kids dealing with JIA.