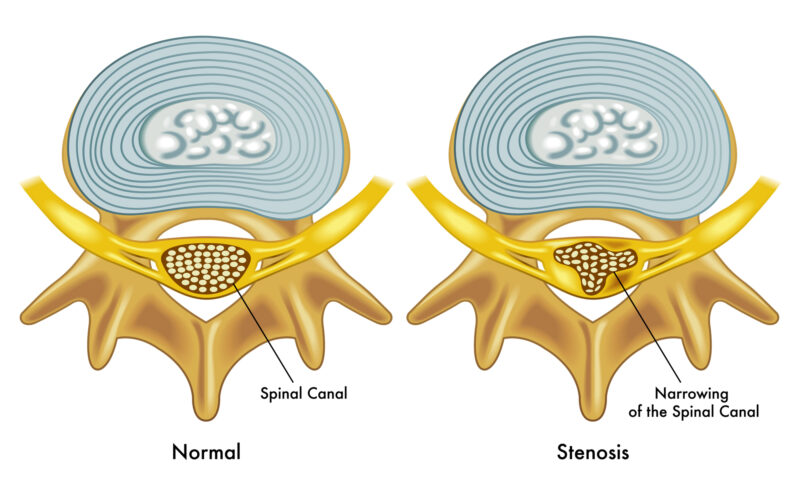
Spinal stenosis, a narrowing of the channel occupied by the backbone, places pressure on the nerves and spinal cord.
The narrowing can occur anywhere along the spine, but most often happens in the low back.
Symptoms
The condition causes low back and leg pain. When the nerves are pinched, sufferers may have numbness, tingling and hot or cold sensations in the legs.
Some people lose control of their muscles, causing falls and difficulty with walking.
Diagnosis
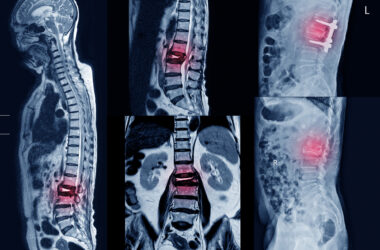
Diagnosis usually begins when a patient complains of leg or low back pain. The doctor may order an imaging test such as an X-ray, MRI or CT scan.
Treatment
Sometimes rest or physical therapy can relieve pain. Changes in posture or performing certain stretches may open space for pinched nerves. Other treatments include:
Medication: Pain may be relieved with anti-inflammatories. NSAIDS, aspirin and ibuprofen are sometimes recommended for back-pain.
Exercise: A physical therapist may recommend certain changes as mentioned previously. In addition, exercises to improve the general strength of the spine may help with pain.
Surgery: If pain persists after other treatments are tried, surgery may be needed. A spinal surgeon will operate to relieve the pressure on the nerve roots. This operation is sometimes done in conjunction with a spinal fusion. Surgery is generally done to lessen pain, weakness or numbness in the legs.
Causes
Spinal stenosis usually develops later in life. Here are some of the most common reasons people develop spinal stenosis:
Age: A host of problems can contribute to spinal stenosis as people grow older. Connective tissues between bones may thicken.
Disks that normally cushion the vertebrae often break down. Bone spurs sometimes develop in the spinal canal.
Tumors: A tumor may cause inflammation in the spinal canal. Tumors also cause problems by growing into the space around the spine. These growths may displace bone or result in bone loss.
Instability: Also called spondylolisthesis, this is a condition where one vertebra migrates onto another vertebrae, causing a narrowing of the spinal canal.
Trauma: Injuries that dislocate that spine or cause fractures can release bone fragments that create pain.
Arthritis: Both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can cause back pain. Osteoarthritis is a joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage.
Cartilage cushions joints and bones, but when it’s damaged, bones don’t slide past one another as they should. Rheumatoid arthritis is a disorder of the immune system which causes swelling and pain in joints.
Heredity: Some people or born with spinal stenosis and begin to suffer symptoms early in life. Some birth defects may also cause the spinal canal to narrow.
Dr. Kuether is a neurosurgeon practicing in Portland, Oregon. He has treated many patients with spinal stenosis.