Today we’re exploring two common spinal surgeries: discectomy and laminectomy. We’ll explore what these procedures do and when these procedures are appropriate for a patient.
As with any surgery, a surgeon and in this case, a neurosurgeon will diagnose and prescribe the best path for your particular situation.
There is no one size fits all solution to spinal procedures and there are a number of factors to consider before performing surgery.
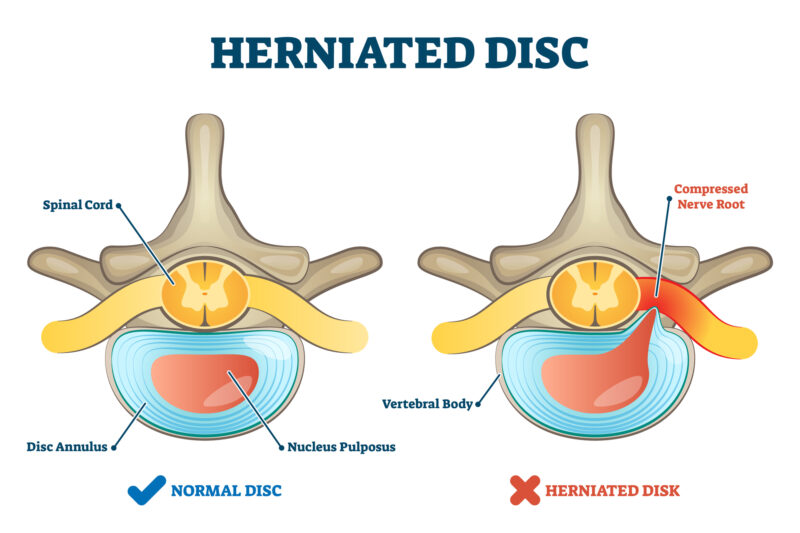
Discectomy is surgery focused on removing a herniated or degenerative disc in the lower spine. The word discectomy literally means – cutting out a disc. While the word is literal, most discectomy procedures include making a posterior incision, through the back muscles, to remove the disc which is pressing on the nerve.
There are multiple techniques for a discectomy including an open or minimally invasive technique.
An open procedure uses a larger incision and muscle retraction to give the neurosurgeon better visibility into the affected area while a minimally invasive technique or microendoscopic discectomy utilizes a small skin incision.
Dilators are then used to tunnel through the muscles where the neurosurgeon will use special instruments to see and operate within a smaller space.
A minimally invasive incision often causes less disruption of the back muscles and can decrease overall recovery time.
A neurosurgeon will determine which technique is more appropriate on a case by case basis.
Discectomy procedures are often recommended for patients who suffer from leg or back pain or have signs of nerve damage in the back or legs.
Physical therapy and medication are often recommended as necessary steps to relieve these issues before surgery.
To be a candidate for discectomy, patients usually suffer from the following symptoms and conditions: a bulging or herniated disc, degenerative disc disease, cauda equina syndrome, significant pain, weakness, or numbness in legs or feet, leg pain (sciatica) worse than back pain or symptoms that have not improved with physical therapy or medication.
The other procedure that we’re exploring today is the laminectomy, which is a surgery that creates space by removing the lamina : the back part of a vertebra that covers the spinal canal.
This surgery is also known as the decompression surgery as it helps to remove or relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
A laminectomy procedure usually includes the patient going under general anesthesia. The neurosurgeon will make an incision in the back over the affected vertebrae and moves the muscles away from your spine as needed.
The surgeon will then use small instruments to remove the appropriate lamina.
Like discectomy procedures, there is an open and a minimally invasive technique.
A neurosurgeon may recommend a laminectomy when more-conservative treatments : such as medication, physical therapy or injections. have failed to relieve symptoms.
Laminectomy may also be recommended if symptoms are severe or worsening dramatically.
The most common cause for spinal pressure is bony overgrowths within the spinal canal. Bone spurs can happen due to aging and arthritis.