When talking about back problems or pain, the phrase herniated disc seems to be a commonly heard and is often pointed to as the source of the trouble, but what is a herniated disc and how does this injury occur?
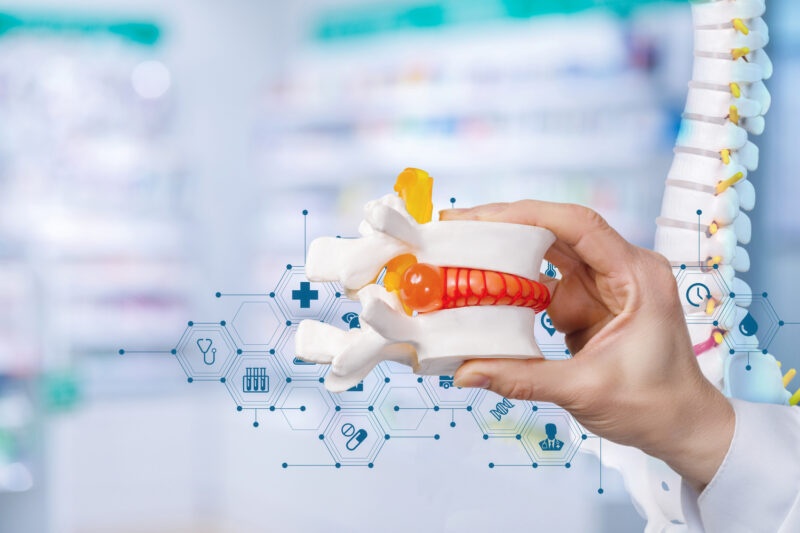
To start, herniated disc refers to one of the rubbery cushions between the spinal vertebrae that bulges or ruptures.
A herniated disc refers to when the softer interior of the disc pushes out through tears in the tough exterior. Herniated discs are most common in the lower back and neck.
A challenging element of herniated discs is that every body reacts differently with some people experiencing excruciating pain with irritated nearby nerves causing numbness or weakness to others who don’t experience any symptoms at all.
Other common symptoms of a herniated disc include weakness due to affected nerves being irritated; numbness or tingling; and arm or leg pain depending on the location of the herniated disc.
If the disc displacement is in a the lower back, patients may feel pain in their buttocks, thighs and calves while if it is in their necks, they may feel pain in their shoulders and arms.
Movement or even just coughing or sneezing can trigger the pain
Now you may wonder what causes a herniated disc?
Unfortunately, it is usually hard to pinpoint one specific incident, but these factors may contribute: gradual, age-related wear and tear; improper + prolonged heavy lifting; or a traumatic injury.
Other risk factors that can increase a person’s chance of a herniated disc include weight, genetic predisposition or occupations that encourage repetitive manual labor with lifting, pulling, pushing, etc.
To identify a herniated disc a neurosurgeon like Dr. Todd Kuether, will use x-ray, CT or CAT scan, MRI or even myelogram or EMG/NCS to diagnosis the location of the herniated disc.
Once identified, treatment will be recommended and luckily for many affected patients, surgery is NOT necessary.
Most herniated discs can be treated with conservative, nonsurgical means such as physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medication or epidural steroid injections.
If surgery is required, there are many options depending on the specific case.
Some of these possible surgeries include artificial disc surgery, discectomy, or spinal fusion. In most cases these are minimally-invasive outpatient procedures.
Again, most herniated discs do not require surgery and can often be managed through physical therapy + pain management.
Herniated discs can also be preventable by avoiding the risks factors and by engaging in the following activities:
- Improving core strength + participating in low stress exercises like swimming, stationary bicycling or walking
- Using correct lifting techniques by squatting to leverage leg strength
- Maintaining proper posture, both when sitting and standing
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce extra strain the body and back
- Quit smoking as it can be a risk factor for lower back pain and degenerative disc disorders
- Avoid prolonged stressful situations as it can lead to muscle tension